1942 - 1947 CHEVROLET SHOP MANUAL
Section 12 - Electrical System
|
|
|||
|
12-9
|
|||
|
|
|||
|
At the same time current flows from the generator
positive to the generator (GEN) terminal of the regulator. From
this terminal a circuit through
the voltage winding of the voltage regulator to
ground and back to the grounded
negative of the
|
voltage winding of the circuit breaker to magnetize
its core sufficiently to attract the circuit breaker armature
and close the points, establishing
a circuit from the generator to the battery as
shown in Fig. 16.
VOLTAGE REGULATOR
It will be noted by
referring to Fig. 18 that the generator voltage is impressed across
the voltage winding of the voltage
regulator at all times. Note also that any change in generator
voltage will make a corresponding
change in the current value passing through the voltage winding of
the regulator. Such being the case, the magnetic strength of
the voltage winding varies
directly as the generator voltage.
As the generator voltage increases to a predetermined
value (7.2 to 7.4) fixed by the regulator
setting, the magnetic pull on the voltage regulator
armature increases until the armature is
attracted toward the core, against
the spring tension, opening the regulator points.
|
||
 |
|||
 |
|||
|
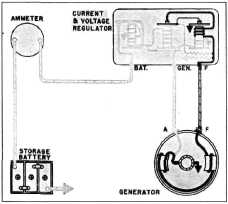
Fig. 17-Field Circuit with Regulator Points
Closed
generator is established. Fig. 18. At the same time
a current flows through the series
windings of both the
current regulator and circuit breaker, thence
|
|||
 |
|||
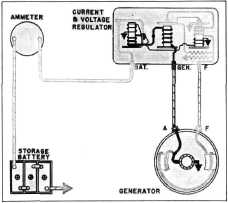
|
Fig. 19-Field Circuit with Voltage Regulator
Points Open
The shunt field circuit must now pass through
the resistance unit, Fig. 19.
This adds to the resistance
of the shunt field circuit, thereby reducing
the current value passing through
the field winding. The
net result of this is a drop in generator voltage. This, in turn,
reduces the current value
passing through the regulator voltage winding,
reducing its magnetic strength,
allowing the spring tension to immediately close the regulator points,
eliminating the resistance
from the field circuit, thus allowing the generator voltage to
build up again. This cycle of
operation occurs many times
per second, resulting in the
voltage being held
practically constant.
|
|||
|
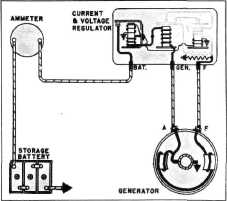
Fig. 18-Voltage Coil Circuit
through the voltage winding of the circuit breaker
to ground and back to the grounded
negative of the generator.
When the engine speed is increased the generator
voltage rises and when it has built up to 6.3
to 6.7 volts, sufficient current
is forced through the
|
|||
|
|
|||