1942 - 1947 CHEVROLET SHOP MANUAL
Section 6 - Engine
|
|
|||
|
6-5 |
|||
|
|
|||
|
5. Expand
the reamer by easy stages and repeat the reaming operation until the piston pin
is fitted.
The proper
fit of the piston pin is a "thumb push" fit as shown in Fig.
6. |
tapered
one thousandth of an inch, being wider at the bottom. With this design the lower edge
of the ring tends to scrape the
excess oil from the cylinder wall and acts as an oil control ring until
the regular oil control ring
is seated (broken-in) in the cylinder. All compression rings
are marked with the word "TOP" cast
in the upper side of the ring. When installing compression rings, make sure
the side marked "Top" is
toward the top of the piston. Chevrolet piston rings are furnished in
standard sizes as well as
.005", .010", .015", .020", .030" and .040" oversizes.
Fitting Piston Rings
To
properly fit new piston rings, proceed as follows:
Slip the
ring into the cylinder then, using the head of a piston, press the ring into the
cylinder bore about two
inches. Using a piston in this way will place the ring square with the cylinder
walls. Now check the space, or
gap. between the ends of the
ring. This should be from .005" to .015".
If the
space between the ends of the ring is less than .005", remove the ring and try another
ring for fit, or the gap in the
tight fitting ring may be enlarged by the following method: Remove
the ring from the cylinder.
Clamp a fine-cut file in the vise. Grasping each end of the ring firmly
between thumb and fingers,
work the two ends of the ring across the surfaces of the file pressing the
ring together at the gap
lightly, until the proper space is obtained. Be careful not to distort the
ring during this operation or
it may bind in the ring groove of the piston. Fit each ring
separately. |
||
 |
|||
|
Fig. 6—Fitting Piston Pin
After
fitting the first piston pin, the other bushings may be reamed
quickly by reducing the diameter
of the reamer by approximately .0005" (half a thousandth) by backing off the expansion
screw. This permits quick roughing-out of all bushings, leaving about half a thousandth for the
finish cut.
It is good
practice to check the diameter of all piston pins with a micrometer. In case
there should be a slight
variation in diameter, this must be taken into consideration when adjusting the
reamer for the finish cut.
The
purpose of the reaming fixture is to make sure that the piston pin bushings will be
reamed at right angles to the
skirt of the piston, assuring proper alignment of the piston in the
cylinder.
Chevrolet
piston pins are serviced in standard sizes as well as .003", .005", and .010"
oversizes.
PISTON RINGS
The
purpose of a piston ring is to take up the space between the cylinder walls and the
piston, to prevent leakage of
gases and oil.
As these
gases are under considerable pressure, it is therefore necessary that the rings
not only fit snugly around the
cylinder walls, but in the grooves of the pistons as well; otherwise
the gases and oil will work by
behind the rings.
The
compression piston ring used in the Chevrolet engine is designed to control oil
consumption during the break-in
period. The face of the ring is |
|||
 |
|||
|
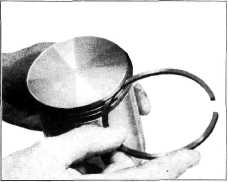
Fig. 7—Rolling Piston Ring in Ring Groove
New piston rings and cylinder
bores wear considerably during
seating and the gaps widen quickly. Engine operation will not
become seriously affected if ring
gaps do not become greater than 1/32". |
|||
|
|
|||